Wastewater Treatment System
MICRO WATER SYSTEM
|
| MICRO WATER SYSTEM |
As environmental pollution escalates, water purification technologies
that emphasize global environment conservation while seeking coexistence
with a natural environment and a recycling-based society are desired. We
offer a chemical-free environmental contaminant elimination system (patented)
that uses an electro-physicochemical reaction. It contributes to conservation
planning for water, space, and electric power, as well as for reduction
of CO2.
|
|
|
|
| Applications |
Cooling tower circulation water treatment, pool circulation water treatment,
boiler water treatment
- Red-rust prevention
- Red-water prevention
- Scale separation and removal。
- Scale removal from pipes
Industrial wastewater treatment system, purification treatment of industrial,
livestock, and water facilities wastewater
Measures for small business wastewater guide
- Manufacturing use
- Organic material separation
- Industrial use
- Food factories wastewater treatment
- Industrial wastewater treatment (factory wastewater treatment)
- Decoloration
- Circulating water treatment
- Measures for total volume regulations
- Wastewater treatment for oil containing water (oil treatment)
- For dairy
- Dairy wastewater treatment (livestock waste water)
- Parlor wastewater treatment
- Decoloration
- Deodorization
- Measures for livestock waste regulations
- Natural Conservation
- Purification of eutrophicated lakes
- Algicidal treatment
- Separation of toxic substances
- Separation/Elimination
- Promoting environment and a recycling-based society and zero emission
- Sterilization of seawater
- Treatment of saline wastewater
It is adjusted for the load and substances.
Some wastewater may not be treatable due to chemicals mixed in. |
 |
 |
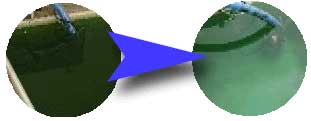
Purification of fire prevention water
(Left: Before Right: After) |
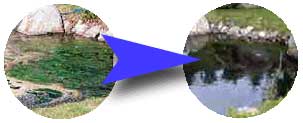
Purification of Lakes
(Left: Before Right: After) |
|
| Effects |
- SS(suspended solids) improvement through electro-physicochemical reaction
- COD(Chemical Oxygen Demand) separation
- Decoloration
- N-Hexane extracts (oil/water separation) separation & removal
- Heavy metal separation & removal
- Mineral separation & removal
- Phosphorus separation & removal
- Nitrogen separation
- Algicidal treatment, algae growth prevention
- Processing water sterilization
- Silica scale separation, collection, and prevention
- Chlorine compounds (dioxins and dioxin-like compounds) decomposition
- Endocrine disruptor degradation
- Ammonia decomposition
- Hydrogen sulfide decomposition
- Cyan component decomposition
- Red rust prevention for pipes (rust-proof)
- Wastewater deodorization
- Advanced wastewater treatment
- Fluoride removal
- Cesium removal
For any questions, please contact us. |
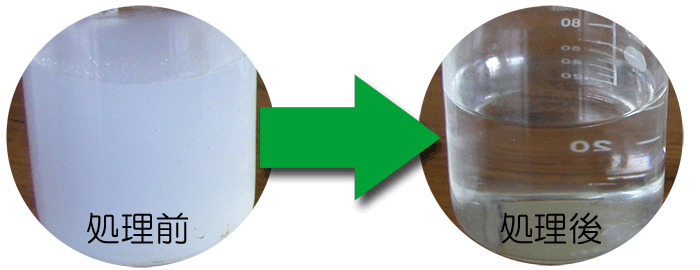 |
| Emulsified cafeteria wastewater |
| Use condition |
- Applicable water: Freshwater, seawater(water and sewer, ground water, industrial
water, river, soft/hard water)
- Applicable temperature: 0 to 90°C
- Capacity: At least several tons (Developed suitable for the conditions.)
- Power: 100V to 440V
|
| Consumables (Maintenance |
| Electrode plates require replacement once in 3 months (or up to 1 year),
depending on the quality of the water. |
| Model Processing Capability |
The processing capability of the patented electrolysis wastewater treatment
system MICRO WATER SYSTEM widely varies, depending on the properties of
water quality and electric conductivity.
1.As industrial or livestock wastewater is directly discharged after the
treatment, facilities with appropriate purification capability are required.
2.Closed circulation water systems, such as cooling towers require less
energy as it takes time (3 days to half month) to improve the quality of
water, and the facility size can be reduced
3.It takes long time (3 months to several years) to gradually produce the
purification effect for lakes and reservoirs, and the facility size and
the power consumption are kept to minimum. If there is a local inflow causing
the contamination, an appropriate system is used to directly purify before
it contaminates lakes.
- Circulation water (cooling tower, etc) total capacity 20t
- Food processing plants -wastewater treatment 100t/day
- Paint wastewater treatment 10t/day
- Livestock wastewater treatment 10t/day
- Recycle of car wash water at gas stations 10t/day
- For other uses, please contact us.
The processing capability is calculated based on the conditions, including
conductivity, temperature, and processing time of the sample water.
Data of the wastewater (pH, conductivity, flow rate, temperature, storage,
circulation/running water, etc) is required.
The sample water for the treatment system is tested for the quality and
the system is designed appropriately for the actual conditions.
|
  |
| CATEGORY |
TEST SAMPLE |
ITEM |
BEFORE TREATMENT |
AFTER TREATMENT |
ELIMINATION RATE (%) |
| Burned Ash |
Treatment of dioxin wastewater |
2378-T4CDD |
21Pg/g |
N.D |
100.0 |
| - |
PCB treatment |
PCB |
0.0040 |
0.0006 |
85 |
| Endocrine Disruptor |
Pre-test data of chlorine-based agricultural chemicals
2 min. x 3 timesPower consumption 10W |
Kelthane |
26 |
4.5 |
82.7 |
| pp’-DDT |
0.21 |
0.11 |
47.6 |
| Endrin |
0.21 |
0.004 |
98.1 |
| Trans- chlordane |
0.48 |
0.042 |
91.3 |
| Food Processing Factory |
Treatment of wastewater from food processing |
COD |
820 |
6 |
99.3 |
| BOD |
520 |
1 |
99.8 |
| SS |
2,000 |
20 |
99.0 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
18 |
0 |
100.0 |
| Nitrogen Content |
100 |
9.8 |
90.2 |
| Kjeldahl Nitrogen |
100 |
0.15 |
99.9 |
| T-P |
23 |
014 |
99.4 |
| Electronics Manufacturer |
Treatment of wastewater from employee cafeteria |
BOD |
89 |
12 |
86.5 |
| COD |
130 |
24 |
81.5 |
| SS |
150 |
14 |
90.7 |
| Nitrogen |
15 |
3.7 |
75.3 |
| Phosphorus |
4 |
0.3 |
92.5 |
| Food Residual |
Digestive fluids from methane fermentation |
BOD |
4,700 |
1,300 |
72.5 |
| COD |
7,700 |
1.000 |
87.1 |
| SS |
15,000 |
230 |
98.5 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
740 |
18 |
97.6 |
| T-N |
2000 |
200 |
90 |
| T-P |
360 |
23 |
93.6 |
| Duct Washer Manufacturer |
Treatment of ventilation duct washing wastewater from kitchens of restaurants
and hotels |
BOD |
120,000 |
1,300 |
99 |
| COD |
42,000 |
980 |
98 |
| SS |
240,000 |
1 |
100 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
170,000 |
6 |
99.9 |
| T-N |
370 |
4.5 |
98.8 |
| T-P |
100 |
1.6 |
98.4 |
| Ground Water |
Treatment of well water |
Ionic silica |
43 |
2 |
95.3 |
| Ca |
14 |
7.6 |
45.7 |
| Amine |
Wastewater of chemical plants |
COD |
70,000 |
2,685 |
96.1 |
| Nuclear-related |
Circulation seawater for cooling fuel bars |
Cesium (test water) |
122.5 |
0.4 |
99.7 |
| Chemical Plants |
Water recovered from scrubber |
Fluorine |
5.500 |
7 |
99,8 |
| Food Processing Plants |
Soy source |
Color |
34.5 |
6.6 |
80 |
| Tap Water |
Plant tap water |
All hardness |
54 |
7.3 |
86.5 |
| Grease Cleaning |
Wastewater of material cleaning |
BOD |
110 |
40 |
63.6 |
| COD |
130 |
52 |
60 |
| SS |
200 |
32 |
84 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
270 |
10 |
96.2 |
| T-P |
1.6 |
0.061 |
96.2 |
| Chemicals |
Treatment of caustic soda wastewater |
COD |
290,000 |
5 |
99.9 |
| Lakes/Ponds |
Lake/pond purification |
SS |
730 |
13 |
98.2 |
| COD |
61 |
17 |
72.1 |
| T-N |
3.1 |
0.83 |
73.2 |
| T-P |
0.48 |
0.16 |
66.7 |
| Total Iron |
240 |
6.4 |
97.3 |
| Coliforms |
70,000 |
1.8 |
100.0 |
| Soy Sources |
Processed water |
SS |
1,480 |
5 |
99.7 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
39 |
10 |
74.4 |
| Dairy/Livestock Wastewater Treatment |
Pigs |
T-N |
1,700 |
130 |
92.4 |
| T-P |
87 |
2.1 |
97.6 |
| Cows |
COD |
22,800 |
154 |
99.3 |
| Machining |
Treatment of wastewater from compressors |
N-Hexane Extracts |
1,100 |
2.5 |
99.8 |
| Waste Soil |
Treatment of mineral oil wastewater |
SS |
19,100 |
17 |
99.9 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
7,500 |
51 |
99.3 |
| Paint Shops |
Treatment of paint wastewater |
COD |
3,680 |
1,080 |
70.7 |
| Pulp Plants |
Treatment of wastewater |
COD |
2,785 |
4.5 |
99.8 |
| Fluorine |
280 |
3.9 |
98.6 |
| Chemical Plants |
Treatment of wastewater |
Ammonia |
15 |
0 |
100.0 |
| Chemical Plants |
Treatment of wastewater |
COD |
56 |
7 |
87.5 |
| TOC |
214 |
88 |
58.9 |
| N-Hexane Extracts |
185 |
5 |
97.3 |
| Total iron |
6.3 |
<0.1 |
99.8 |
| Metal Plating Factory |
Treatment of wastewater from nickel |
Nickel component |
5,400 |
16.1 |
99.7 |
| Cyanogen |
13.7 |
<0.1 |
99.3 |
| Cyanogen |
10,000 |
0.6 |
99.9 |
| Heavy Metals |
Treatment of cleaning water for soldering |
Copper |
1.8 |
<0.02 |
98.9 |
| Lead |
0.03 |
<0.005 |
83.3 |
| Public Bath |
Treatment of bath wastewater |
Legionella |
1,800 |
0 |
100.0 |
| Bacteria |
Results of joint verification study with Advanced Industrial Science and
Technology |
Legionella |
460,000 |
0 |
100.0 |
| Staphylococcus Aureus |
47,000 |
0 |
100.0 |
| Salmonella |
460,000 |
0 |
100.0 |
| E.cO157 |
98,000 |
0 |
100.0 |
Unit: mg/L (Unless otherwise specified.)
Removal rate is not guaranteed because the data depends on the quality
of water. |
|
| Attaching to existing equipment |
Electrolytic bathes are additionally installed.
Modifications to the existing processing bath, storage bath, and/or settling
tanks are also available. |
| Installation Cost |
Installation Cost of Wastewater, Effluent Treatment
Since the conditions of wastewater widely vary depending on actual sites,
the purification test is required for each case/condition.
Take appropriate measures to keep the characteristics of water constant
over time, it changes.
Purification lab test (with charge) is required for the estimation of the
initial facility cost and running cost in order to provide appropriate
quotations, considering factors including property of wastewater, processing
amount, desire purification level, concentration, water quality items,
and installation sites.
(Purification guarantee is not available unless water quality is tested.)
Cost Reduction in Wastewater Treatment
Instead of dilution, incineration, distillation & concentration, or
industrial waste disposal, raw wastewater is detoxified and purified to
reduce the cost and load to environment (dilution water, fuel, CO2). |
|
Installation Cost to Cooling Tower (Total Water storage amount 20t)
We will estimate the cost appropriately for each site. |
|
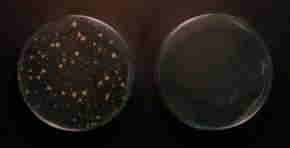
| Bacteria elimination and sterilization of water using the MICRO WATER SYSTEM® |
- Sterilization effect has been verified using high-efficient electrolysis
system, MICRO WATER SYSTEM ® at Industrial Technology Institute of Ibaraki
Prefecture (April 24, 2000).
- Sterilization effect for legionella, salmonella, staphylococcus aureus,
and O-157 has been verified. (March 2001) National Institute of Advanced
Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
|
 |
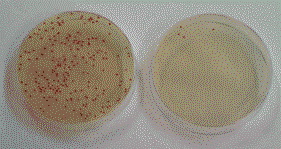 |
| Legionella |
Common Bacteria |
|
Cooling Tower Circulation Water Electrolytic Sterilization Test
(Japanese home appliance manufacturer in Indonesia, Cooling tower water |
 |
|
MICRO WATER SYSTEM |
Chemical Treatment |
| Common Bacteria(CFU/ml) |
1.3×102 |
2.7×104 |
| Coliforms(CFU/ml) |
- |
- |
|
|
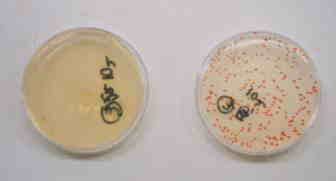
| Electrolytic Sterilization of Public Bath |
 |
Hot spring water in the Kanto region
- Raw water (right)
- Electrolyzed water (left)
| Sample No/Number of detections |
Common Bacteria |
Legionella |
Coliforms |
| Hot spring water (Kanto region) |
1.5×104 |
140 |
- |
| After Processed |
3.5×102 |
- |
- |
|
|
 |
Public bath in Kanto region
- Raw water (right)
- Electrolyzed water (left)
| Sample No/Number of detections |
Common Bacteria |
Legionella |
Coliforms |
| Public bath (Kanto region) |
3.6×105 |
- |
- |
| After Processed |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
 |
Public bath in Shikoku region
- Raw water (right)
- Electrolyzed water (left)
| Sample No/Number of detections |
Common Bacteria |
Legionella |
Coliforms |
| Public bath (Shikoku region) |
2.4×104 |
20 |
- |
| After Processed |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
 |
Hot spring water in the Shinshu region
- Raw water (right)
- Electrolyzed water (left)
| Sample No/Number of detections |
Common Bacteria |
Legionella |
Coliforms |
| Hot spring water (Shinshu region) |
1.1×104 |
560 |
- |
| After Processed |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|
| Removing red-rust through electrolysis process |
Red-rust protection using the(MICRO WATER SYSTEM)
Red rust on pipes and facilities of cooling towers are removed without
using chemicals. For instance, rust on the facilities caused by the Thailand
flood can be easily removed using electrolyzed water processed by our electrolysis
equipment. |

|
Elapsed Time |
Condition |
| Photo (left) |
After 2 hours in the electrolyzed water |
Red rust was removed. |
| Photo (right) |
After 22 hours in the electrolyzed water |
Red rust was removed and black rust appears. |
|
 |
- Red rust was removed, and solid and liquid were separated.
- Rust on the parts soaked into water was removed.
- Changed to black rust which prevents development of red-rust.
|
|
 |
Rusted iron bars were soaked in tap water and electrolyzed water and observed.
- Top: Before processing, Before soaking
- Bottom: After 1 month
|
Processing Method |
Condition |
| Photo (left): |
Soaked in tap water. |
Red-rust was slightly removed. |
| Photo (center): |
Soaked in electrolyzed water. |
Red-rust was removed. Partially became black rust. |
| Photo (right): |
Not processed. |
No change |
|
|
Patent No US6,706,168B2
特許第3635349号
特許第6343760号 |
|
|
|
| Copyright (C) IGADEN CO.,LTD. All Rights Reserved. |
|
| Contact idj@igaden.com |
|













